Navigating JupyterLab#
JupyterLab is a web-based interface containing a file explorer and a code editor that supports Python, Julia, and various other languages.
File management#
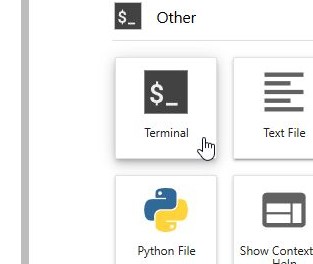
To open the Terminal:
To open the File Browser, click the folder icon on the left sidebar.
To enter a folder, double-click on it.
To enter a parent directory, a directory in the path of your location e.g. a folder containing the currently open folder: click on the name of the directory in the path above the column headers in the File Browser.
To upload a file to the current location, click on the upload icon above the path.
To delete, rename, etc. a file, right-click on a file or directory.
To paste copied file(s), right-click anywhere under the column header, then click Paste.
To open project directories located outside your home directory (/$HOME or users/username) in the File Browser, you will need to create a symlink.
Click the plus sign at the top of the File Browser to open a new Launcher tab.
Click the Terminal button to open a new Terminal tab.
Copy and paste
ln -s "<project directory>" ~/<new directory name>into the Terminal, replacing<project directory>with the path of your project directory and/<new directory name>with the desired position of the link in your $HOME directory. Press Enter.Navigate to the path of the symlink. Click the refresh button in the top right corner of the File Browser if required.
The project directory can now be opened in the File Browser by double clicking the symlink.
Code editing#
Jupyter contains cells that can be run individually. These cells can run either markdown or the language of the Kernel visible in top right corner of a .ipynb document tab. Python3 comes already installed with JupyterLab. Cells can also contain Magic Commands that are outside the standard functionality of Python.
To open a new notebook:
Run options can be chosen by clicking the ‘Run’ tab in line with the Jupyter logo at the top, then clicking the desired run option.
To save or create a new checkpoint, click on the memory card icon under the .ipynb tab or simultaneously press the Ctrl and S keys.
Cell operations like creating cells, copying them, etc. can be done by clicking on the ‘Edit’ tab in line with the Jupyter logo at the top, and then clicking the desired operation.
To open a new Python file, open the Launcher tab, then click on Python File under Other.

To run a Python file:
Method 1:
Open a Terminal.
Type
python path_to_py_file, replacingpath_to_py_filewith the path to the Python file.Press Enter. The output is displayed within the Terminal.
Method 2:
Open a notebook.
Copy and paste the following in a separate line of a cell, replacing
path_to_py_filewith the relative path to the Python file:%run path_to_py_file
Run the cell. The output for the Python file is displayed under the cell.
Additional Help#
This website contains in-depth instructions on navigating JupyterLab Notebooks.