Introduction to GitHub and Getting Setup#
Getting Started with GitHub#
Initial Setup of Your Repository and Python Environment#
Go to the GitHub repository for our class Jupyter notebooks.
Select “Fork”. This will create a personal copy of the repository.
Select “Code” and copy the HTTPS URL for the forked repository.
Go to the HPC Portal and log in.
Select “Clusters” and then “M3 Shell Access”.
In the terminal session, type each command and press Enter:
tmux
git clone "paste the URL for the forked repository here"
cd ds_1300_notebooks
git remote add upstream https://github.com/SouthernMethodistUniversity/ds_1300_notebooks.git
misc/repo_to_ssh # Follow prompts
mkdir work
module load conda
mamba env create -f environment.yml --force
exit
Launching a JupyterLab Session#
Via Conda (Mamba) Environment#
Go to the HPC Portal and log in.
Select “Interactive Apps” and then “JupyterLab”.
Set the fields to:
“Partition”:
standard-s“Select Python Environment”:
(Conda Env) ds_1300“Time (Hours)”
4“Timeout (minutes)”:
60“Cores per node”:
4“Memory”:
16
Select “Launch” and wait for the job and JupyterLab session to begin (this can take a few minutes).
Select “Connect to JupyterLab”, which will appear when the JupyterLab session has started.
Select the “File Browser” icon at the top of the left sidebar and browse to your
ds_1300_notebooksdirectory.
Via Container#
Go to the HPC Portal and log in.
Select “Interactive Apps” and then “JupyterLab”.
Set the fields to:
“Partition”:
standard-s“Select Python Environment”:
Custom Environment - only use what is specified below“Custom environment settings”:
module purge
module use /work/classes/ds_1300/modules
module load ds_1300
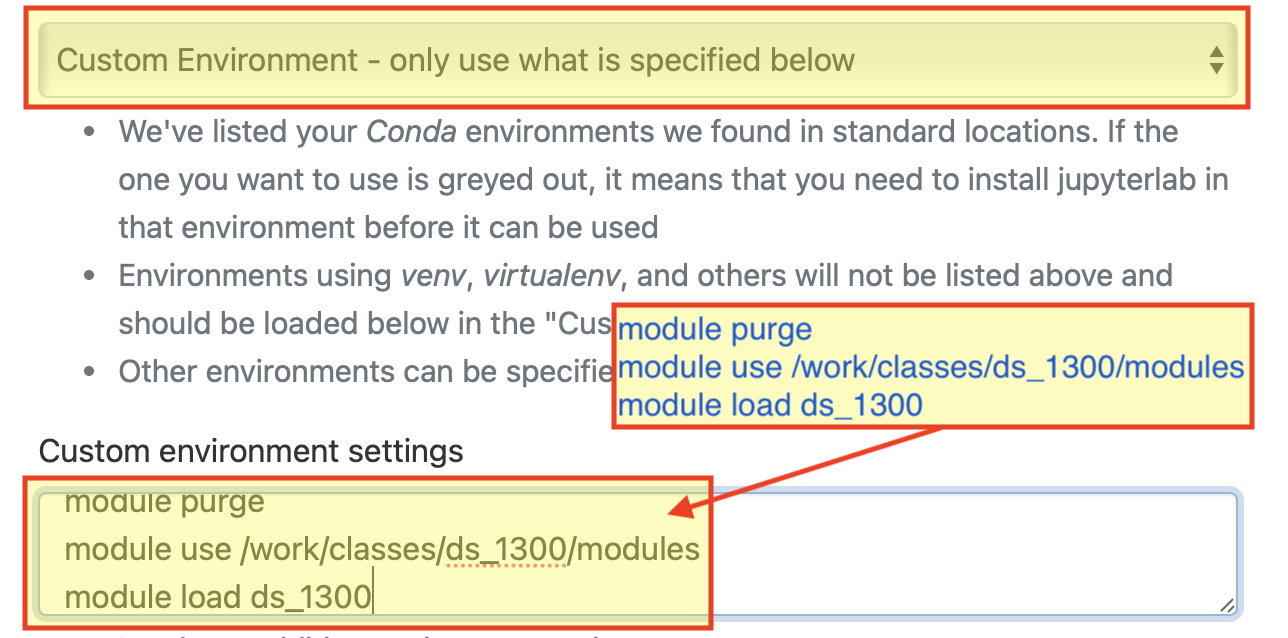
Fig. 1 DS 1300 container environment.#
“Time (Hours)”
4“Timeout (minutes)”:
60“Cores per node”:
4“Memory”:
16
Select “Launch” and wait for the job and JupyterLab session to begin (this can take a few minutes).
Select “Connect to JupyterLab”, which will appear when the JupyterLab session has started.
Select the “File Browser” icon at the top of the left sidebar and browse to your
ds_1300_notebooksdirectory.
Working on Notebooks#
Browser into “code” directory.
Right-click on a notebook and select “Copy”.
Browse into your “work” directory.
Right-click with the directory and select “Paste”.
Double click the notebook to open.
Pulling New Notebooks#
Save the notebook.
Open a terminal session via “File”, “New”, “Terminal”.
In the terminal session, type each command and press Enter after each line:
cd ds_1300_notebooks
git fetch upstream
git stash push -- $(<.gitignore)
git merge upstream/main -m "Merge from upstream."
Note
If you have edited a file tracked upstream, e.g.
code/01_assignment.ipynb, you won’t be able to merge. Checkout the file to clear the changes, e.g.git checkout code/01_assignment.ipynb, and then proceed withgit merge upstream/main -m "Merge from upstream.".If the above doesn’t work, first verify that all notebooks that you want to save are in your
workdirectory, then rungit reset --hard, and then proceed with the fetch and merge steps.
Installing New Packages#
New Python packages can be installed allowing you to build upon the work of
others. Both methods should be run from the Terminal from within the Jupyter
Lab session. Installing packages directly via pip is the suggested procedure
for the class when installing your personaly selected packges, while
installation via the requirements.txt should be reserved for packages pushed
from upstream.
Open a terminal session via “File”, “New”, “Terminal”.
In the terminal session, type each command and press Enter after each line:
New Packages via pip#
cd ds_1300_notebooks
pip install <package_name>
New Packages via requirements.txt#
Before executing the following commands do the “Pulling New Notebooks” commands
above first. This will make sure that you have the most recent version of the
requirements.txt file available to you.
cd ds_1300_notebooks
pip install --ignore-installed -r requirements.txt
Submitting Completed Assignments via GitHub#
Save the notebook.
Open a terminal session via “File”, “New”, “Terminal”.
In the terminal session, type each command and press Enter after each line:
cd ds_1300_notebooks
git add work/<the name of the completed notebook without brackets>.ipynb
git commit -m "<Brief note about work witout brackets>"
git push
git tag -a <assignment number without brackets> -m "<Completed assignment number without brackets>"
git push --tags
Add Dr. Godat and Dr. Kalescky to Your Forked GitHub Repository#
Log into GitHub
Go to your ds_1300_notebooks repository
Select “Settings”
Select “Manage access” on the left-side panel
Select “Invite a collaborator”
Type “egodat” in the field and then select “Eric Godat” when it appears
Select “Add egodat to this repository”
Select “Invite a collaborator”
Type “rkalescky” in the field and then select “Robert Kalescky” when it appears
Select “Add rkalescky to this repository”